(a) Isolation of human adipose-derived stem cells from fat tissue by membrane filtration method
Human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) are easily isolated from fat tissue without ethical concerns, but differ in purity, pluripotency, and differentiation ability, depending on the isolation method. We developed an isolation method of hADSCs from a primary fat tissue solution using a membrane filtration method and a membrane migration method. hADSCs where the primary cell solution was permeated through membranes, adhered hADSCs were cultured, and hADSCs migrated out from the membranes. hADSCs isolated by the membrane migration method had the highest stem cell surface marker expression and efficient differentiation into osteoblasts. The membrane filtration and migration method will open avenue for the clinical application of hADSC transplantation more easily and with high purity of stem cells.
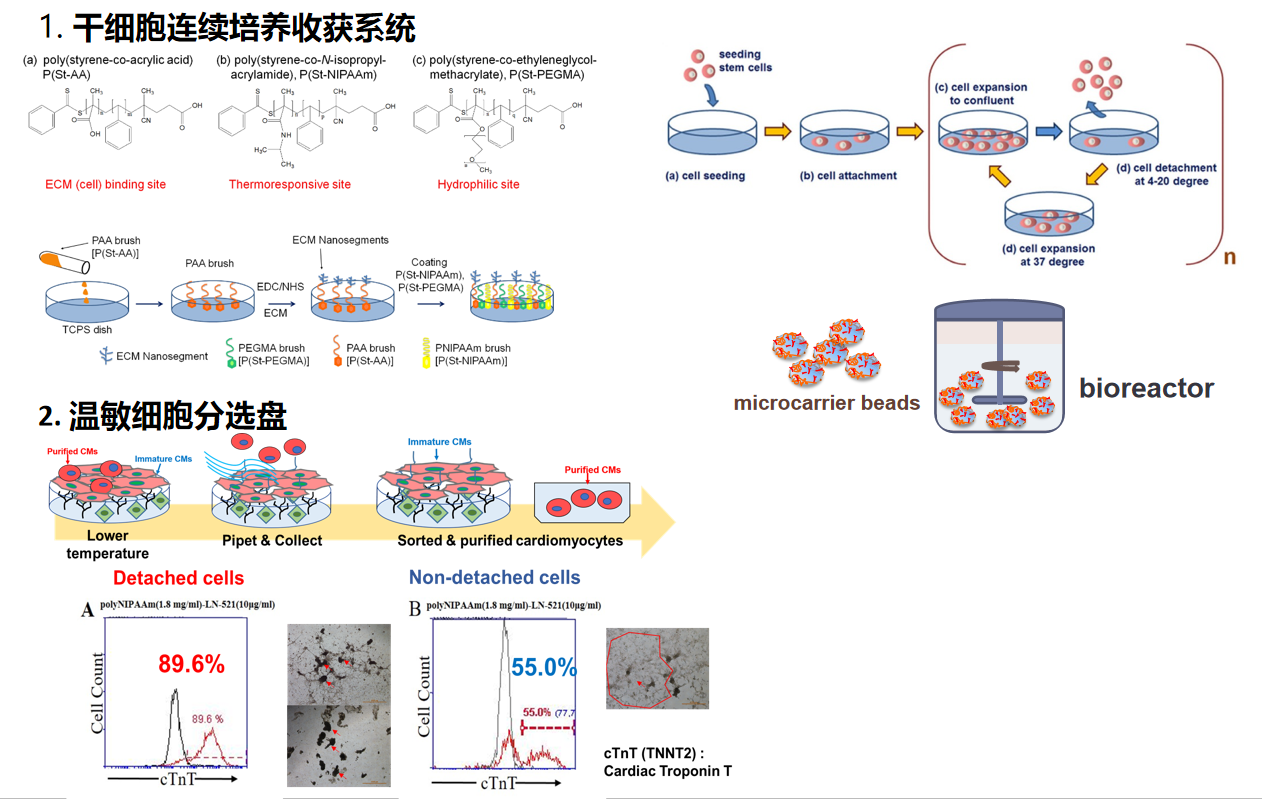
(b) Development of cell culture materials for expansion and differentiation of human embryonic stem (ES) cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells
Current xeno-free and chemically defined culture and differentiation methods of hPSCs (human pluripotent stem cells) are not efficient and sometimes not reproducible. Therefore, it is necessary to develop reliable and efficient culture and differentiation methods of hPSCs for future usage in clinical application. We developed a continuous culture method of hPSCs on the dishes immobilized with thermoresponsive nanosegment where a continuous culture method was the first time developed by our group (Prof. Higuchi). We also developed a coating nanosegment materials for hPSC culture in xeno-free culture conditions. Currently, we are developing optimal cell culture materials for hPSC differentiation into cardiomyocyte and retinal pigment epithelium.
(c) Development of cell sorting dishes, which can deplete or concentrate cancer stem cells from tumor
Cancer-initiating cells [cancer stem cells (CSCs)] in colon cancer cells can be selectively suppressed when they are cultured on Pluronic (nanosegment)-grafted dishes, whereas CSCs are maintained on conventional tissue culture dishes and extracellular matrix-coated dishes. CSCs persist in tumors as a distinct population and cause relapse and metastasis by giving rise to new tumorigenic clones. The purification or depletion (suppression) of CSCs should be useful for analyzing CSC characteristics and for clinical application. CSCs can be selectively suppressed from human colon cancer cells containing human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) on Pluronic-grafted dishes (cell sorting dishes), while hADSCs remain on the dishes. hADSCs on Pluronic-grafted dishes after the suppression of the CSCs can differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, cardiomyocytes, and neuronal cells. The CSCs and hADSCs exhibited different characteristics. The selection of hADSCs is possible on Pluronic-grafted dishes that suppressed the CSCs from the fat tissues of cancer patients (i.e., cell-sorting dishes). We are also developing cell sorting dishes for isolation of CSCs.
(d) Preparation of retinal pigment epithelium differentiated from human ES and iPS cells as well as human amniotic fluid stem cells on optimal cell culture biomaterials for treatment of patients with macular degeneration
Current clinical trials that evaluate human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-based therapies predominantly target treating macular degeneration of the eyes because the eye is an isolated tissue and generates a low immunoreaction in nature. Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) differentiated from hPSCs is typically used in most clinical trials for treating patients, whereas bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMNCs) or mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are intravitreally transplanted, undifferentiated, into patient eyes. We are now developing efficient differentiation method of hPSC-derived RPE and RPE differentiated from human amniotic fluid stem cells, which were cultured on optimal cell culture biomaterials for future cilinical application of RPE transplantation into patients having macular degeneration.
 (a) Isolation of human adipose-derived stem cells from fat tissue by membrane filtration method
(a) Isolation of human adipose-derived stem cells from fat tissue by membrane filtration method Dept: International Affairs Dept. (Office of HongKong, Macao and Taiwan Affairs)
Dept: International Affairs Dept. (Office of HongKong, Macao and Taiwan Affairs) Tel: 86-577-8807 5587
Tel: 86-577-8807 5587 Address: 270 West Xueyuan Road, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
Address: 270 West Xueyuan Road, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China